- Home
- Technological sources
- Extended planar magnetrons
Extended planar magnetrons
Magnetron sputtering devices are designed for sputtering electrically conductive targets made of metals, alloys, semiconductor materials in DC sputtering modes, pulsed unipolar and bipolar, dual medium-frequency modes. Magnetron discharge takes place in crossed electric and magnetic fields.
Magnetrons are widely used for the application of the following coatings:
- Metal: Ti, Cr, Zr, Al, in “hot” mode, Ni, Co, stainless steel.
These coatings are used as adhesive, functional layers in optics, microelectronics, when applying hardening coatings and other fields.
- Semiconductor: Si, Ge, ZnO, ZnS, SiC and other coatings used as functional layers in microelectronics.
- Ceramic: TiN, AlTiN, TixOy, AlTiSiN, TiCN, CrxOy, Al2O3 and many others used as hardening, protective decorative, photocatalytic coatings (tools, dies, molds, furniture and door fittings, decorative ceramics)
Fig. 1 shows a diagram of one version of an extended planar magnetron
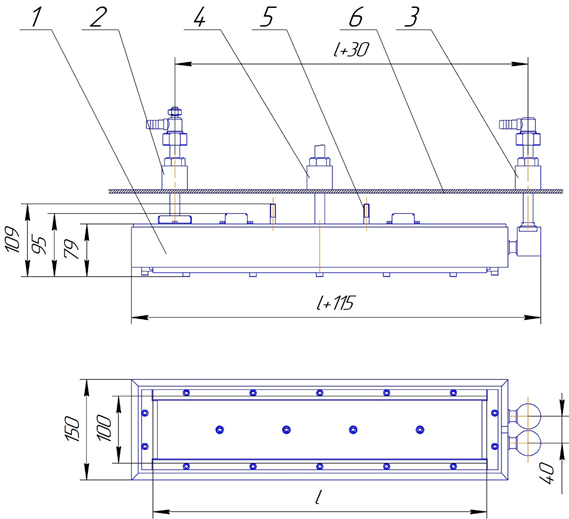
Fig. 1 Magnetron diagram 1 – water cooled housing, 2 – high-voltage input, 3 – cooling input of housing 4 – plasma-forming gas inlet, 5 – magnetron hanger, 6 – vacuum chamber walls
Planar extended magnetrons are classified according to the type of magnetic system as follows:
- Magnetron with an unbalanced magnetic system characterized by additional ion bombardment of a substrate. Characteristics of unbalanced planar magnetrons. The properties of coatings applied using reactive processes (nitrides, oxides, carbides, carbonitrides and oxy nitrides) are significantly higher when using magnetrons with an unbalanced magnetic system than when using balanced magnetrons due to increased ionization of the plasma-forming gas and the sputtered target material.
- A magnetron with a balanced magnetic system is characterized by a smaller effect of ions on a substrate.
Characteristics of balanced planar magnetrons
|
No. |
Parameter |
Value |
|
1 |
Operating pressure, Pa |
0.07– 0.15 |
|
2 |
Target length of manufactured magnetrons, mm |
from 250 to 3500 |
|
3 |
Average energy of argon ions at a voltage of up to 500 V, eV; |
up to 400 |
|
4 |
Current density per unit length of the erosion zone with a width of the erosion zone of 35 mm, mA/cm |
up to 120 |
|
5 |
Magnetic field uniformity along the length (option), % |
±3 (±1.5) |
|
6 |
Power density per unit area of the erosion zone, W/cm2 |
50 |
|
7 |
Deposition rate at a target to substrate distance of 120 mm - titanium target μm/h; - zirconium target μm/h; |
5 10 |
|
8 |
Ratio of the current density of gas ions and sputtered target atoms /density of flux of sputtered atoms at a bias voltage of -100 V |
up to 0.5 |
|
9 |
Target utilization rate (option), % |
20-40 (70) |
|
10 |
Plasma-forming gases |
inert gases, oxygen, nitrogen, hydrocarbons |
There are two design versions of the magnetron input
1. Magnetron with cooling and power supply connections on the rear side (on the one side in the case of single-circuit cooling, and on two opposite sides in the case of dual-circuit cooling, Fig. 1) is connected to cooling and power supply sources using copper tubes in fluoroplastic insulation with seal assemblies designed by the magnetron manufacturer.
Advantages of our magnetrons:
- We provide a magnetron model for design engineers and recommend the optimal target–substrate distance.
- Magnetron magnetic field sputters a strictly defined zone and guarantees the absence of foreign impurities in the substrate and a high utilization rate of the target.
- Galvanic coating of internal cooling cavities of the magnetron and magnetic circuit allows to prolong service life.
- Short lead times.
- Multi-stage quality control.
- Stable behaviour over time.
Our company has developed a series of indirectly cooled magnetrons, where targets are inserted in the form of inserts, which allows to increase the target utilization rate to 70%. This solution also allows to supply the users of magnetrons with targets in the shortest possible time and to reduce the cost of the coating applied, having obtained a competitive advantage. The target of any standard size for this series of magnetrons is picked up from standard inserts. So, this eliminates the long waiting for the target supply and idle time of expensive equipment.
Experience and professionalism of our team allows us not only to manufacture a standard series of magnetrons, but also to conduct R&D of magnetrons of various types and purposes. Currently, several projects are at the design and test stages:
- Magnetron with a “hot” target for sputtering of ferromagnetic materials and deposition of ceramic materials (deposition of rare earth oxides).
- Annular magnetron for deposition of expensive materials.
Contact our company and get a magnetron that is optimally suited to your processes.





